School system
学校制度
がっこうせいど
The nucleus of the school system is the system of six-year elementary schools (children enter school at age 6), three-year junior high schools, three-year high schools, and four-year universities. In addition there are kindergartens, five-year technical colleges (koto senmon gakko) for graduates of junior high school, special training schools (senshu gakko) , and schools for children with disabilities (mo-ro-yogo gakko). Universities include undergraduate colleges, junior colleges, and graduate schools. Education is compulsory through junior high school, and over 99% of elementary school and 93% of junior high schools are public; private schools play a larger role at the secondary and university level (24% of Japan's high schools and 73% of its universities are private institutions).
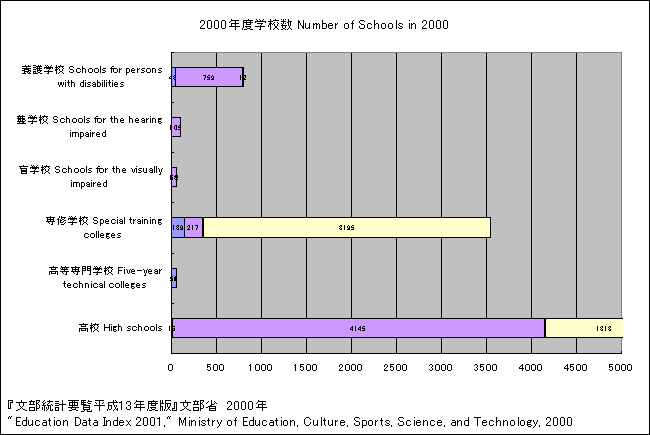
| Table: Number of Schools in 2000 | | High schools | 5,478 (15 national, 4,145 public, 1,318 private) | | Five-year technical colleges | 62 (54 national, 5 public, 3 private) | | Special training colleges | 3,551 (139 national, 217 public, 3,195 private) | | Schools for people with disabilities | 71 schools for the visually impaired (1 national, 68 public, 2 private) | | Schools for the hearing impaired | 107 (1 national, 105 public, 1 private) | | Schools for persons with disabilities | 814 (43 national, 759 public, 12 private) |
|
|